Maximizing Energy Efficiency with Heat Recovery Ventilation Systems
Discover the benefits of heat recovery ventilation and how it can enhance your energy efficiency.
Energy efficiency is becoming increasingly important as we strive to reduce our impact on the environment and save money on energy costs. One way to improve energy efficiency in buildings is through the use of heat recovery ventilation systems. These systems not only improve energy efficiency but also improve indoor air quality. In this article, we will explore the importance of energy efficiency, the benefits of heat recovery ventilation systems, how they work, the different types available, and successful case studies.
KERS HEAT RECOVERY
Understanding the Importance of Energy Efficiency
Energy consumption has a significant impact on the environment and economy. The burning of fossil fuels for energy releases greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, contributing to climate change. Additionally, energy costs can be a significant expense for individuals and businesses. Improving energy efficiency can help reduce energy consumption, lower costs, and reduce our impact on the environment.
There are many benefits to improving energy efficiency. For individuals, it can mean lower energy bills and a more comfortable living environment. For businesses, it can mean lower operating costs and improved productivity. Additionally, improving energy efficiency can create jobs in the energy efficiency industry and reduce our dependence on foreign oil.
Introduction to Heat Recovery Ventilation Systems
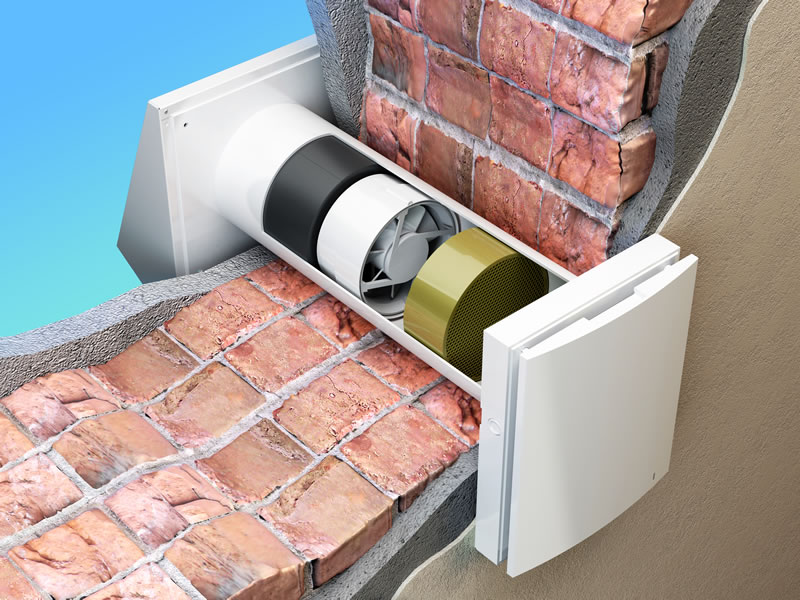
Heat recovery ventilation systems are a type of mechanical ventilation system that improves energy efficiency by recovering heat from the exhaust air and using it to preheat incoming fresh air. These systems also improve indoor air quality by providing fresh air and removing stale air.
How Heat Recovery Ventilation Systems Work
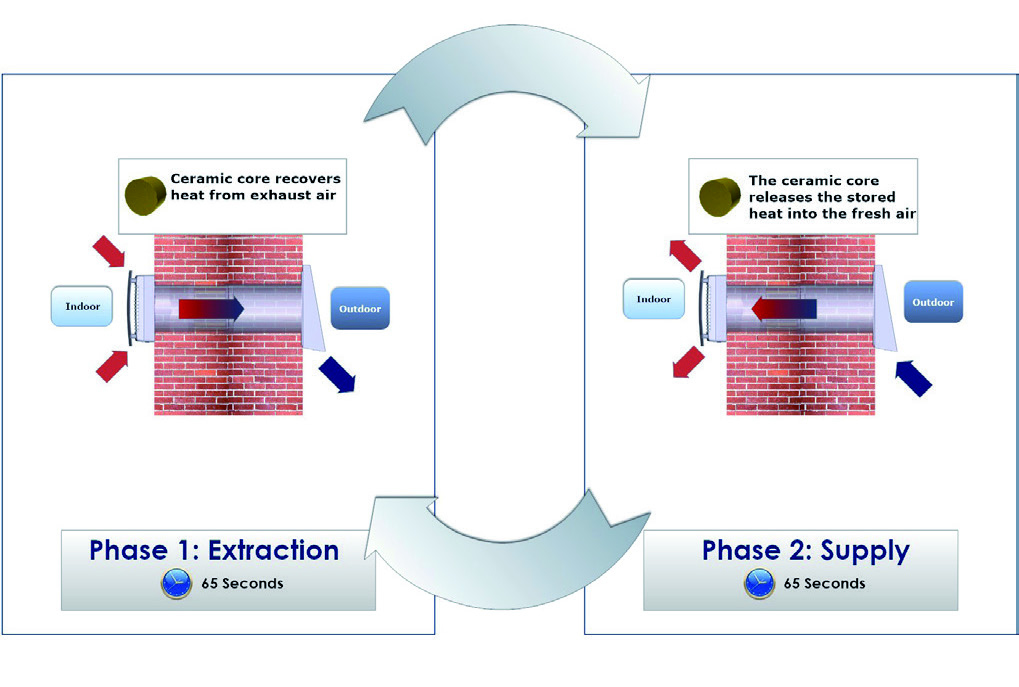
Heat recovery ventilation systems work by using a heat exchanger to transfer heat from the exhaust air to the incoming fresh air. The heat exchanger is typically made of a material that conducts heat well, such as aluminum or copper. The incoming fresh air is preheated by the exhaust air, reducing the amount of energy needed to heat the air to the desired temperature.
In addition to the heat exchanger, heat recovery ventilation systems typically include a fan to circulate the air, filters to remove pollutants and allergens, and controls to regulate the system.
Benefits of Heat Recovery Ventilation Systems
There are many benefits to using heat recovery ventilation systems. They improve energy efficiency by reducing the amount of energy needed to heat the incoming fresh air. They also improve indoor air quality by providing fresh air and removing stale air. This can reduce the risk of indoor air pollution and improve the health and comfort of building occupants.
Additionally, heat recovery ventilation systems can help reduce noise pollution by providing a quieter alternative to opening windows for ventilation. They can also help reduce the risk of condensation and mold growth by controlling humidity levels.
Types of Heat Recovery Ventilation Systems
There are several types of heat recovery ventilation systems available, including:
– Cross-flow heat exchangers: These systems use a flat plate heat exchanger to transfer heat from the exhaust air to the incoming fresh air.
– Rotary heat exchangers: These systems use a rotating wheel to transfer heat from the exhaust air to the incoming fresh air.
– Run-around coil systems: These systems use a coil to transfer heat from the exhaust air to a separate coil in the incoming fresh air stream.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Heat Recovery Ventilation System
When selecting a heat recovery ventilation system, there are several factors to consider, including:
– Building size and layout
– Occupancy levels
– Climate
– Budget
– Maintenance requirements
It is important to select a system that is appropriate for the specific building and meets the needs of the occupants.
Installation and Maintenance of Heat Recovery Ventilation Systems
The installation process for heat recovery ventilation systems typically involves cutting holes in the walls or roof for the ductwork and installing the system components. It is important to ensure that the system is installed correctly to ensure optimal performance.
Maintenance requirements for heat recovery ventilation systems typically include replacing filters, cleaning the heat exchanger, and checking the controls. Regular maintenance can help ensure that the system is functioning properly and improve its lifespan.
Maximizing Energy Efficiency with Heat Recovery Ventilation Systems
To maximize energy efficiency with heat recovery ventilation systems, it is important to ensure that the system is properly sized for the building and that the controls are set correctly. It is also important to ensure that the system is maintained regularly to ensure optimal performance.
Additionally, it is important to consider other energy-efficient measures, such as insulation and air sealing, to further improve energy efficiency.
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Heat Recovery Ventilation Systems
There are many examples of successful implementation of heat recovery ventilation systems in different buildings. For example, a school in the UK installed a heat recovery ventilation system and saw a 30% reduction in energy consumption and improved indoor air quality. A hospital in Canada installed a heat recovery ventilation system and saw a 50% reduction in energy consumption and improved indoor air quality.
Conclusion: The Future of Energy Efficiency with Heat Recovery Ventilation Systems
Heat recovery ventilation systems are an effective way to improve energy efficiency and indoor air quality in buildings. As we strive to reduce our impact on the environment and save money on energy costs, these systems will become increasingly important. By selecting the appropriate system, ensuring proper installation and maintenance, and considering other energy-efficient measures, we can maximize the benefits of heat recovery ventilation systems and contribute to a more sustainable future.
- Find out more about
- KERS Heat Recovery








